Introduction
We would remember the times when grocery lists were an ubiquitous phenomenon. The local grocer or the kirana was the recipient of these lists at the beginning of every month from households in the catchment area he served. The need to deliver these lists in person or over the phone to the grocer for pick-up or delivery later in the day is slowly starting to become a thing of the past. Grocery marketplaces, some with instantaneous delivery options (quick commerce), have offered an abundance of convenience to the Indian customer. The easiest way to shop has become via the smartphone and essentials reach home in as little a time as 10 minutes. Convenience and technology led order placement is not limited to the end user and is also an option for the grocer. B2B digital marketplaces have disrupted the traditional FMCG distribution channels. The pace of this disruption and the subsequent channel conflict it has triggered has asked more questions than FMCG companies have answers to. This article analyses the genesis of these conflicts and predicts the direction the FMCG distribution model is likely to take going forward.
E-Commerce is outpacing traditional channels in the $110Bn FMCG market
The Indian FMCG market was valued at US $110 Bn in 2020 and is expected to double by 2025 to $220 Bn1. This growth is being driven by growth in rural markets, which are forecasted to beat the urban markets in consumption by 2025. FMCG retail landscape in India is dominated by traditional trade with its mom-and pop stores sells which accounts for ~86% the market (Fig 1). Digital channels including E-Commerce and D2C (Direct to Consumer) are growing much faster than the traditional channels, with Accenture estimating that top FMCG companies derive ~7 – 8%2 of sales from these channels. Marico’s E-Commerce business contributed ~1% in FY173 and has grown to 8% by FY214. Dabur’s E-Commerce business has tripled in saliency from ~2% in Q2FY21 to ~6% in Q2FY225. ITC has seen similar progress with the digital channels contributing to 7% in Q2FY226 as against 5% in FY21 and ~2.5% in FY207. This increase is spurred by the disruption by marketplace platforms such as Big Basket, Udaan, Dunzo, Amazon Pantry, Flipkart, Jio Mart.
General Trade Modern Trade E- Commerce
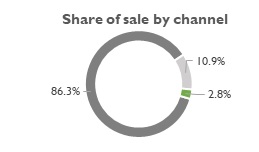
Fig 1: FMCG sales split by Channel – 2020
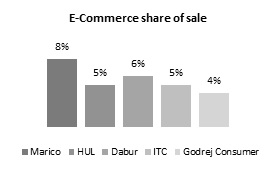
Fig 2: E-Com contribution in leading FMCG firms
With the ease of access to digital infrastructure, there has been a rise in the number of internet users. According to the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), there were 448 Mn active social media users in India in February 2021. This in turn has influenced online shopping trends with social media being the biggest customer acquisition channel. On the other end of the shopping spectrum, lies the General or Traditional Trade.
The general trade with ~13 million outlets and Modern trade with ~18,000 outlets (as per Nielsen estimates) sold FMCG products to customer. With the advent of technology, a customer today can approach alternate channels such as social media, marketplace platforms or company websites and apps for their favorite brands. Social commerce, reseller models and O2O (Online to Offline) have emerged as popular alternative channels in China and have enabled disruption across all retail categories – Food to Furniture to Fashion. The FMCG distribution model in India now has at least 7 unique channels, substantial in market size as shown in Fig 3.
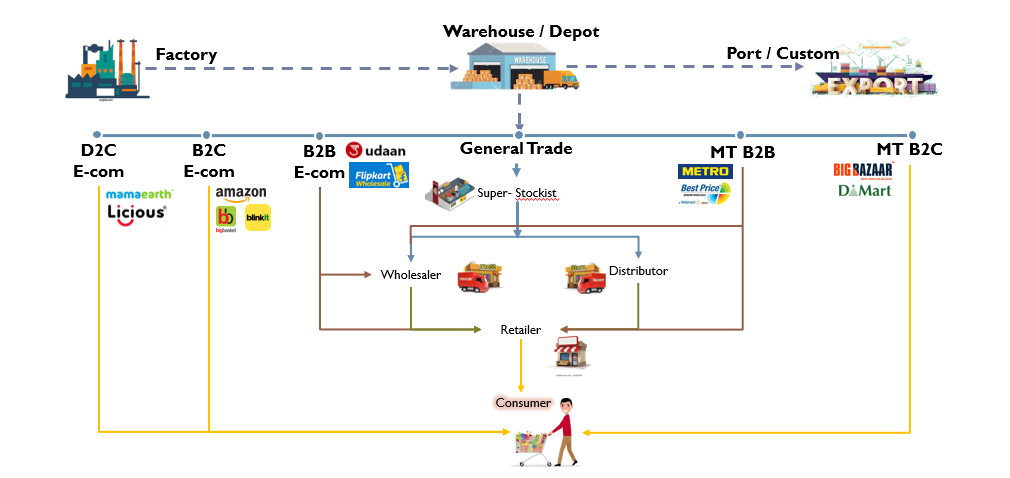
Figure 3: FMCG Distribution Channels
Coverage gaps and enhanced technology penetration enabling B2B E-Commerce advent
With the advent of new channels – D2C, E-Commerce – the FMCG customer or channel partner is set to gravitate towards to online channels steadily over time. This migration is expected to be sharper in urban markets, accentuated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The Chinese Urban FMCG market has seen a near 20%+ increased contribution from E-Commerce in a mere 5 year period (Fig 4), with a growth rate of nearly 35% YoY. The Indian economy is expected to follow a similar trend, even if not at such a frenetic pace.
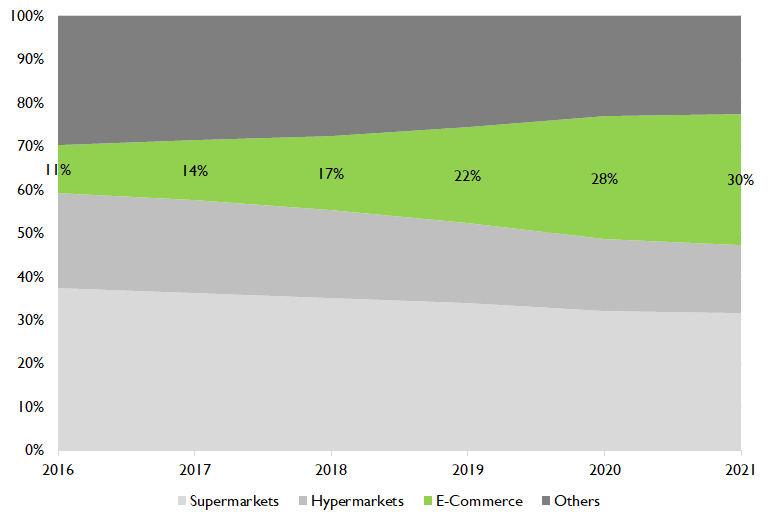
Fig 4. Share of retail sale by channel – China FMCG Urban market
Traditional distribution channels in India contribute to 86% of the FMCG business but direct penetration of even FMCG leaders are ~60% (Fig 5). FMCG companies have coaxed, incentivized and disincentivized traditional distributions to ensure direct coverage, only for the distributors & wholesalers to successfully argue against it with the financial unviability of a direct distribution model. While a vast majority of the remaining 40%, primarily in rural geographies, get covered through indirect distribution (wholesalers, retailer -> retailer purchase), challenges remain in logistics, lower margins for channel partners and higher than MRP prices for customers.
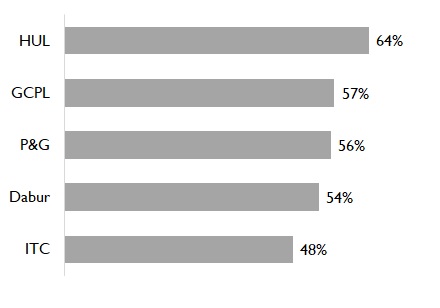
Fig. 5. Direct Customer Penetration
These challenges have paved the way for B2B E-Commerce firms to enter, disrupt, plug coverage gaps and offer value added services to both FMCG companies & retailers. Companies like Elastic Run, Udaan, Jio Mart are being operated on this premise and are unicorns today.
Rise of channel conflict between traditional distributors and B2B e-commerce
With the emergence of B2B E-Commerce, urban markets have emerged early adopters, transferring a share of the pie from traditional distributors to these online platforms. Competition has given way to channel conflict and the FMCG firms are caught in the crosshairs. The new year of 2022 brought new challenge for major brands. In the month of January, distributors in Maharastra9, went on a strike and stopped selling HUL products, followed by distributors of colgate palmolive. Dhairyashil Patil, President of The All India Consumer Product Distributors Federation10 and The Maharashtra State Consumer Product Distributors Federation (MCPDF), told Business Line that the decision was taken due to brands refusal to engage with them on their concerns regarding the lack of price parity between traditional distributors and organised B2B distributors (Jio Mart, Metro, Walmart and Udaan).
All India consumer products distributor federation11 alleged that FMCG companies were selling products at lower prices to B2B distributors and further the organized B2B distributors were selling the same products to retailers at a lower price. In response to the AICPDFs concerns, Amul and Parle have stopped direct supply to Udaan12. Other large FMCG organizations such as HUL, Marico have acknowledged the issue publicly and have promised credible steps13 to support fair returns on investment for their general trade distribution channel.
We at Qwixpert have spent time analyzing the issue in depth and also offer solutions to FMCG organizations to address channel conflict.
The E-commerce distribution model offers an attractive value proposition
Let us start by understanding the operating model and value proposition of emerging B2B distributors such as Jio Mart, Udaan, Elastic Run and others, to both the FMCG players (suppliers) and Retailers (customers). Convenience through technology enablement, value added services and network effects of supply & demand consolidation are core principles of operation (Fig 6).
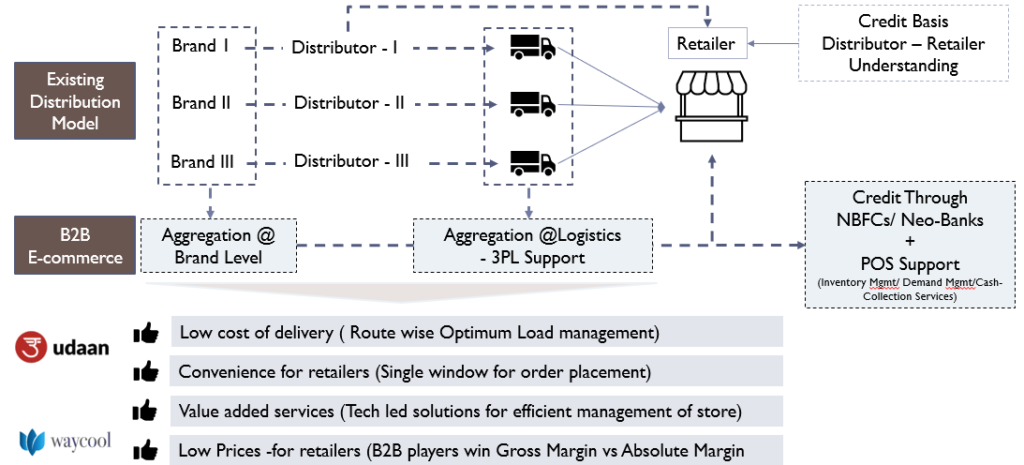
Fig 6: Value proposition – B2B E-Commerce
- Multicategory demand aggregation – unlike traditional distributors B2B E-commerce players are product category and brand agnostic leading to many advantages.
- Retail & geographic demand aggregation reducing unit cost of logistics
- Ability to pass on lower cost of operations to retailers by offering higher margins
- Optimized outbound logistics for FMCG brands – B2B E-Com players can in the future replace super stockists & stockists, reducing cost & complexity in downstream operations
- Enhanced penetration and coverage – Shared logistics across categories and retailers allow B2B E-Commerce players to viably supply rural & remote geographies
- Door-step delivery – No more visits to multiple wholesalers will unburden retailers
- Credit facility – Partnerships with financial institutions (including new age fintech firms) offer similar or better credit options to retailers in comparison to the GT distributor’s terms or those from local unorganized networks
- Value added services – With the use of IT based solutions, B2B e-commerce players offer full stack app-based platform to place purchase orders and other services such as billing software, stock return indents, inventory management, fintech linked cash & loan collection, automated order replenishmen
B2B E-commerce business’ income streams threatens multiple business models
The value proposition, as noted above, substantially elevates the nature of competition to traditional distribution channels. This coupled with the potential to derive income from several new income streams can alter the very foundation of FMCG distribution in India.
Control over the demand data allows B2B E-commerce players to offer Private Label products, especially in categories with lower brand loyalty. This will adversely affect revenues of FMCG brands. Partnership fees with various service providers who digitize general trade operations – accounting, financial services, inventory & demand management. Some companies have even launched their own fintech arms. The digital platform and marketplace business model offers monetization opportunities – digital marketing – search & display ads, brand promotions, charges on fulfilment services, listing & discovery fees, sale of demand data post analytics to brands.
These income streams disrupt multiple industries and functions – Asset light approach to retail sale data will impact retail research agencies like Nielsen and Kantar, Private Label sales opportunities will promote massive contract manufacturing opportunities for MSMEs and demand aggregation may make sales organizations leaner in traditional FMCG firms. The general trade distribution model also offered higher visibility over retailer sales data with sales people collecting & servicing orders. Loss of control over this data gold mine and the evidenced success of private label in global markets, have made FMCG firms circumspect.
FMCG brands can invest in assets, new partnerships & technology to address conflict
Despite general trade being the major source of distribution in India for decades, ~50 – 60% direct retail coverage creates a just cause for E-commerce businesses. The growing Indian market allows for both traditional and e-commerce channels to co-exist profitably although the status quo will have to change. FMCG brands can take several steps to resolve channel conflict and achieve inclusive growth across channels.
Channel conflict is not new to FMCG business – was seen when modern trade emerged. Most notably, consumer electronics has seen an aggressive version of this conflict with the emergence of E-Com marketplace platforms.
- Channel exclusivity among products and categories is often the preferred solution. However, this solution may not offer long term equilibrium in the current environment.
- FMCG firms are also experimenting with a direct to retailer delivery model, which bypasses the traditional distributor in their value chain. Thereby ensuring full visibility over demand data. Asian paints has successfully been operating this model for several years, offering higher service levels & customer satisfaction to its retailer partners. Qwixpert is engaged with a leading FMCG brand in evaluating this distribution model.
- Direct to retailer distribution model also needs a relook at warehouse networks – locationally, structurally and operationally. Investment in technology, Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems, Robotic picking, conveying and sortation systems, become critical to manage higher order complexity & throughput.
- Co-opetition (Collaborate competition) among brands are critical to support traditional distributors. Demand aggregation among FMCG brands in non-competing categories by offering multi-brand distribution will improve General Trade distributor RoI. Co-opetition is not new to the distribution business environment. Automotive (Eg: Autonation, Penske) and consumer electronics (Eg: Redington, Ingram) players have long followed this in the west. Best practices from these models can be identified and emulated.
- Technology enablement of General Trade Distributors is another solution. Leveraging 3rd part services from logistics (eg: Delhivery, Shadowfax) to facilitate last mile delivery with synergies in demand aggregation, Point of Sale technology solutions (payment gateways, order management, fulfilment, accounting & GST filing) and fintech partnerships for easy credit can ease the burden on distributors both operationally and financially. Working capital locked up can be freed and profit margins become higher.
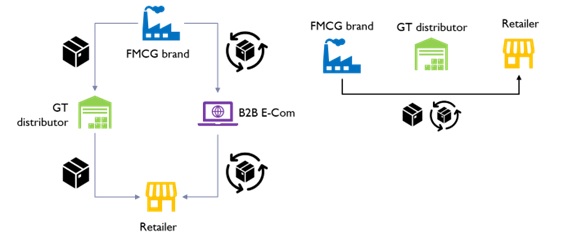
Fig 7: Channel exclusivity and Direct to Retailer distribution
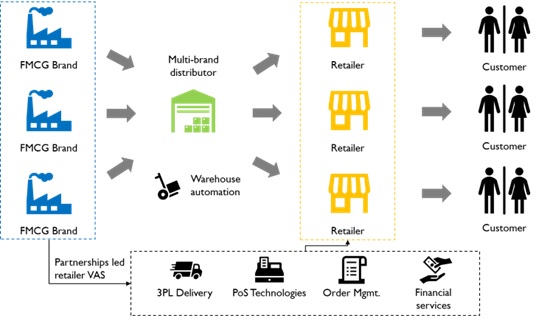
Fig 8: Multi-brand General Trade distribution system with Competitive services
Conclusion
Technology adoption in the country is rising at a frenetic pace. With the emergence of B2B marketplaces, traditional processes have been disrupted and the ensuing channel conflict is now unavoidable. The future state of equilibrium will iron out inefficiencies but must ensure an equal competitive platform for traditional and online marketplace channels. A win-win scenario does exist but it is not a quick fix. The higher degree of convenience and lower cost of service will gravitate retailers towards to B2B E-Commerce companies unless the FMCG brands and distributors equip themselves adequately.
The traditional channel of distribution must undergo massive changes in its operating model to remain competitive. FMCG companies must invest in distributor operating model upgrades. Partnerships with fintech, logistics and point of sale technologies will equip general trade distributors to compete with online channels and also reduce their costs and working capital pressures. Consolidation of general trade distribution similar to global models in automotive and electronics industries is expected.
– Giridharan Raghunathan and Ayushi Barnwal
Sources:
1. https://www.ibef.org/download/FMCG-September-2021.pdf
2. https://www.livemint.com/industry/retail/ecommerce-emerging-as-bigger-retail-channel-11623690512609.html
3. https://marico.com/investorspdf/Marico_-_Harnessing_Digital_-_Arisaig_Partners_Consumer_Symposium_2017_-_September_17.pdf
4. https://www.livemint.com/companies/news/heres-how-much-e-commerce-is-contributing-to-sales-of-large-fmcg-companies-11626611943905.html
5. https://www.businesstoday.in/latest/corporate/story/dabur-india-q2-profit-rises-20-to-rs-482-crore-e-commerce-biz-grows-over-200-277548-2020-11-03
6. https://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/itc-doesn-t-rule-out-listing-infotech-biz-open-to-creating-value-for-fmcg-121121401480_1.html
7. https://www.livemint.com/industry/retail/itcs-fmcg-sales-via-e-commerce-doubled-in-fy21-11626348915830.html
8. https://www.bain.com/insights/a-sudden-slowdown-in-2021-fmcg-recovery/
9. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/companies/now-distributors-to-block-hul-colgate-products-in-4-more-states/article38094485.ece
10. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/companies/after-hul-maharashtra-distributors-to-stop-selling-products-of-other-fmcgs/article38081998.ece
11. https://www.livemint.com/industry/retail/fmcg-distributors-seek-level-playing-field-threaten-firms-of-noncooperation-11638771763050.html
12. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/startups/amul-parle-others-stop-direct-supply-to-b2b-startup-udaan/articleshow/85964942.cms
13. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/companies/after-hul-maharashtra-distributors-to-stop-selling-products-of-other-fmcgs/article38081998.ece


